new 对象的执行过程
创建一个新对象:new操作符会创建一个新对象,该对象会继承自构造函数的原型对象。
设置对象的原型:新对象的
__proto__属性会被设置为构造函数的原型对象prototype。执行构造函数:构造函数会被执行,
this指向新创建的对象。在构造函数内部,可以通过this关键字来添加属性和方法到新对象中。对构造函数有返回值的处理判断:
- 如果构造函数没有显式地返回对象,返回新创建的对象;(基本类型忽略)
- 如果构造函数返回了一个对象,则返回该对象。(引用类型返回)
js
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
const person = new Person('Alice', 18)
console.log(person) // { name: 'Alice', age: 18 }
// new Person('Alice', 18)会创建一个新的对象,并执行Person函数,将this关键字指向新对象。最后返回新对象,赋值给变量person。原型和原型链
作用:解决构造函数浪费内存问题,实现对象属性和方法的共享。
js
function Star() {
}
const star1 = new Star()
// star1.__proto__ === star1.constructor.prototype
Star === Start.prototype.constructor
// Object.prototype.__proto__ // null
Object instanceof Function // Object顶级对象是 顶级构造器 Fcuntion 的实例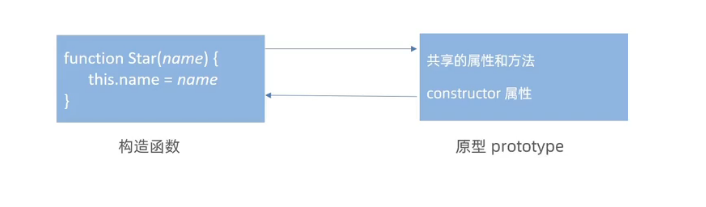


函数的隐式原型对象
js
function test() {}
// test.__proto__ == Function.prototype // ture本身 ---> 构造函数.prototype(本身.__proto__) ---> 构造函数原型对象的原型.prototype.__proto__...--->Object.prototype ---> null
JS继承有哪些方式
方式一:ES6
js
class Parent {
constructor() {
this.age = 18
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
constructor() {
super()
this.name = '张三'
}
}
const o1 = new Child()
console.log(o1, o1.name, o1.age)方式二:原型链继承
js
function Parent() {
this.age = 20
}
function Child() {
this.name = '张三'
}
// 子构造函数原型对象指向父构造函数实例
Child.prototype = new Parent()
const o2 = new Child()
console.log(o2, o2.name, o2.age)方式三:借用构造函数继承
js
function Parent() {
this.age = 22
}
function Child() {
this.name = '张三'
Parent.call(this)
}
const o3 = new Child()
console.log(o3, o3.name, o3.age)